MicroBlaze Processor Product Guide
Providing information about the 32-bit and 64-bit soft processor, MicroBlaze, which is included in AMD Vivado.

A Flexible and Efficient Soft Processor
The AMD MicroBlaze™ processor offers a range of customizable, easy-to-integrate, 32-bit/64-bit microprocessor configurations based on the efficient RISC Harvard architecture. The MicroBlaze processor offers flexibility, allowing for a wide range of customizations with peripheral, memory, and interface features. With its adaptable nature, the MicroBlaze processor has proven to be beneficial for a variety of applications across multiple areas, including industrial, medical, automotive, consumer, and communication markets.
Tried, tested, and trusted, the MicroBlaze processor has a timeless appeal that spans across generations. It has found its way into many applications over the years. Its enduring design and reliable performance have built a strong loyalty among customers, who repeatedly choose the MicroBlaze processor for its consistent reliability and proven success.
Developers can target the MicroBlaze processor to any AMD adaptive SoC or FPGA device supported by the Vivado™ Design Suite at no extra cost. It is also available as part of the legacy Integrated Design Software (IDS) embedded edition for older FPGA families like the Spartan™ 6 FPGA.
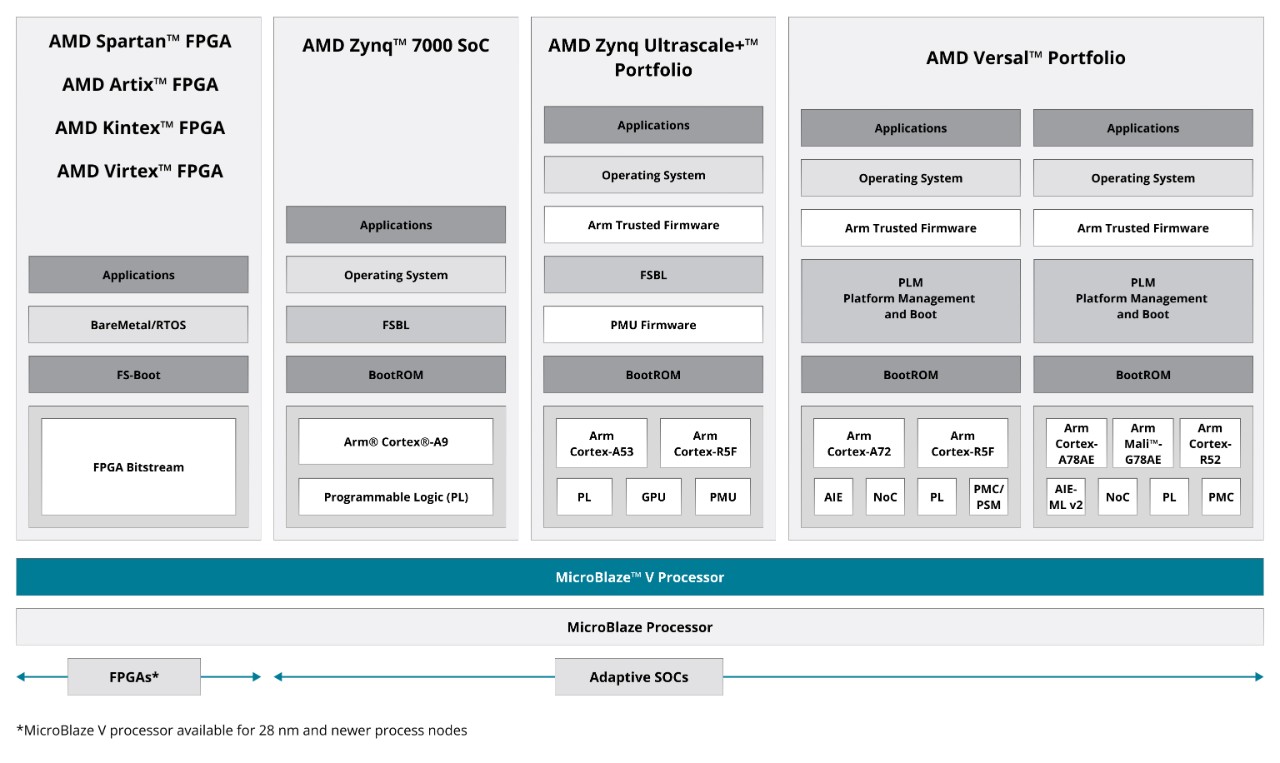

Discover the potential of the AMD MicroBlaze™ V processor. Bringing RISC-V open-source benefits, easy hardware migration, design portability, and a comprehensive industry-backed ecosystem, this processor streamlines your design and offers optimal efficiency and safety features.
| Device | Microcontroller (1.09 DMIPs/MHz) |
Real-Time Processor (1.38 DMIPs/MHz) |
Applications Processor (1.38 DMIPs/MHz) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fmax | DMIPS | Fmax | DMIPS | Fmax | DMIPS | |
| Cost-Optimized Portfolio Devices | ||||||
| Spartan™ 7 (-2) FPGA | 186 | 203 | 152 | 210 | 132 | 182 |
| Artix™ 7 (-3) FPGA | 203 | 221 | 181 | 250 | 140 | 193 |
| Zynq™ 7000S (-2) SoC | 186 | 203 | 155 | 214 | 128 | 177 |
| Zynq 7000 (-3) SoC | 211 | 230 | 171 | 236 | 147 | 203 |
| FPGAs, 3D ICs, MPSoCs, and Adaptive SoCs | ||||||
| Kintex™ 7 (-3) FPGA | 295 | 322 | 243 | 335 | 204 | 282 |
| Virtex™ 7 (-3) FPGA | 299 | 326 | 252 | 348 | 202 | 279 |
| Kintex UltraScale™ (-3) FPGA | 392 | 427 | 291 | 402 | 244 | 337 |
| Virtex UltraScale (-3) FPGA | 384 | 419 | 283 | 391 | 243 | 335 |
| Kintex UltraScale+™ (-3) FPGA | 519 | 566 | 390 | 538 | 343 | 473 |
| Virtex UltraScale+ (-3) FPGA | 517 | 564 | 377 | 520 | 338 | 466 |
| Artix UltraScale+ (-2) FPGA | 482 | 525 | 358 | 494 | 300 | 414 |
| Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC (-3) | 518 | 565 | 365 | 504 | 334 | 461 |
| Versal™ AI Core Series (-3HP) | 437 | 476 | 361 | 498 | 310 | 428 |
Based on AMD internal testing in November 2023, using the Dhrystone benchmark V2.1 to test an AMD MicroBlaze processor with predefined presets and allowed compiler options, and using the GNU tool chain provided in AMD Vivado 2023.2 IDE. Actual results may vary. (IP-001)